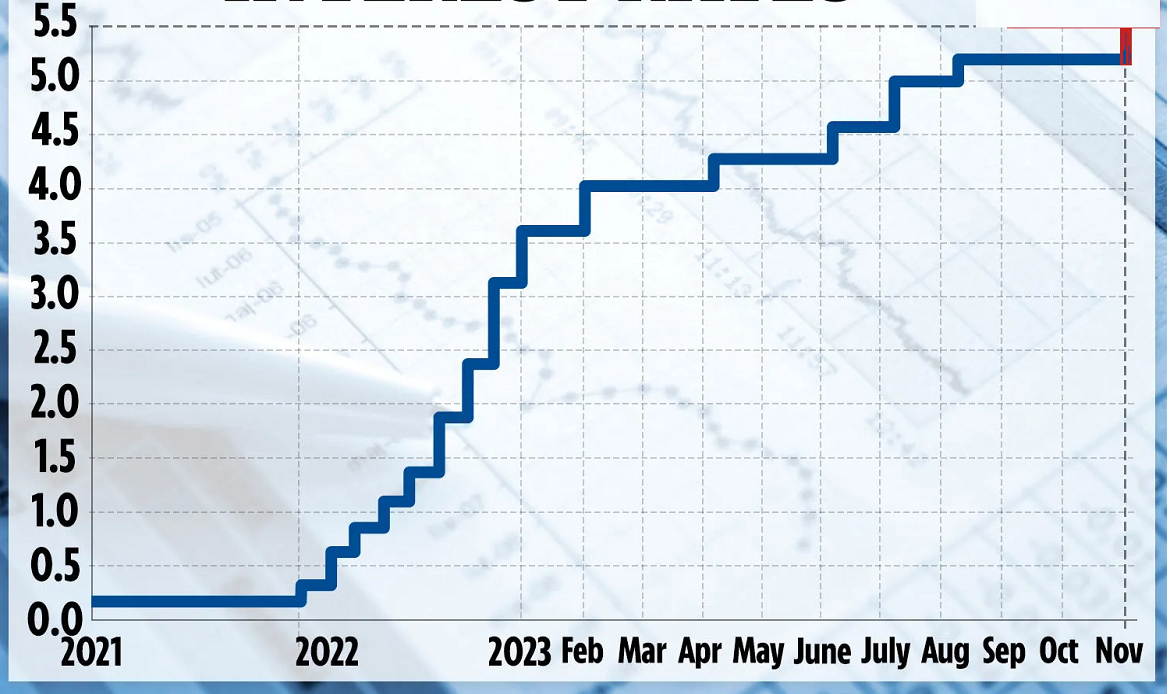
The interest rate which is set and used by banks and financial institutions as a basis for determining their lending rates, that is, for pricing loans and similar products. It should not be confused with the prime rate, which refers to the average interest rate charged by banks on loans to prime customers (the prime rate is an average for the banking industry and will vary from bank to bank). The base rate represents the minimum rate of interest possible on a loan, and reflects the state of the market. In the U.K, banks used, in the past, a system called “prime lending rate” to determine their lending rates, but many banks manipulated this system to offer unsustainably discounted lending rates for borrowers. Offering loans with much cheaper prices to attract customers, especially those without adequate levels of creditworthiness, resulted in numerous cases of default by customers who were unable to repay the loans.
The base rate system, as opposed to the prime lending rate system, restricts variance on interest rates charged on loans. However, there are some types of loans that are not (or cannot be) priced using the base rate system, including agricultural loans, employee loans, export credit, loans against deposit, etc. The calculation of base rates takes into account the cost of deposits and cost of idle cash kept aside to meet cash reserve ratios and withdrawals (a bank may calculate the base rate based on past six-month deposits). The base rate also includes other elements, as defined from time to time by monetary authorities, of which are adjustment for the negative carry in respect of cash reserves and liquidity, unallocatable overhead costs for banks (such as legal and premises expenses, advertising and communications costs, IT spending, depreciation, deposit insurance, etc), and profit margin.
From a British regulatory perspective, the base rate refers to the rate at which the Bank of England lends to the discount houses, so that it effectively controls the interest rates charged throughout the banking system.