A multi-asset option is one whose payout depends on the overall performance of more than one underlying asset. In addition to first-order greeks, second-order greeks, and third-order greeks, there are greeks that relate to the cross effects and the sensitivity to the correlation between two or more assets on which an option is written. In other words, if the value of an option depends on, or is determined by, two or more underlyings, its greeks are extended to take into account the cross effects and correlations between the underlyings. The main cross greeks include: cross gamma, cross vanna, cross zomma, correlation delta, cross vomma (cross volga), and cross speed.
| Cross greek | Formula | Measures: |
|---|---|---|
| Cross gamma | 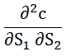 |
Rate of change of delta in one underlying in response to a change in the level of another underlying |
| Cross vanna | 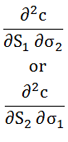 |
Rate of change of vega in one underlying in response to a change in the level of another underlying |
| Cross zomma | 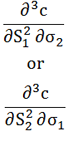 |
Rate of change of gamma in one underlying in response to a change in the volatility of another underlying |
| Correlation delta | 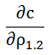 |
Sensitivity of option value to a change in the correlation between the underlyings |
| Cross vomma | 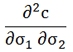 |
Rate of change of vega in one underlying in response to a change in the volatility of another underlying |
| Cross speed | 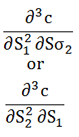 |
Rate of change of gamma in one underlying in response to a change in the level of another underlying |
All these cross greeks can be computed using the mixed numerical greeks.





Comments