A tool that measures the amount of change in the delta of a derivative (most often an option) in response to a unit change in the underlying asset’s price. Differently stated, an option’s gamma is the rate of change in its delta (delta refers to the option’s sensitivity to changes in the the underlying). Mathematically, gamma is the second partial derivative of the option price with respect to the underlying price. For a European option, gamma is given by:
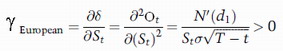
Where :Ot is the option’s price, St is the underlying price, T-t is the option’s time to maturity, σ is the underlying’s standard deviation (volatility), and d1 is defined as follows:
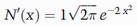
Gamma is identical for European calls and puts.
The maximum value of gamma is attained when an option is at the money, and it decreases as an option moves away from its strike price (at-the-money options close to maturity have big gammas). The nearer an option to its expiration date, the higher its gamma, and vice versa.
Gamma is also known the delta of delta.






