An alternative set of Greeks, literally mixed Greeks, (alternative to the so-called analytical Greeks) that are derived and calculated numerically using a valuation model (for a derivative). This involves calculation of a Greek based on more than a factor, deriving it once for a factor and again for another. Examples of mixed numerical Greeks include: charm and DdeltaDvol. Charm is the second-order derivative of the option value, once to the underlying price and once to the time decay, whereas, DdeltaDvol measures the changes in delta resulting from changes in volatility levels. Delta, per se, captures the change in an option’s price (or generally a derivative‘s) for a small change in the underlying price or rate.
In numerical calculation, for example, DdeltaDvol is given by:
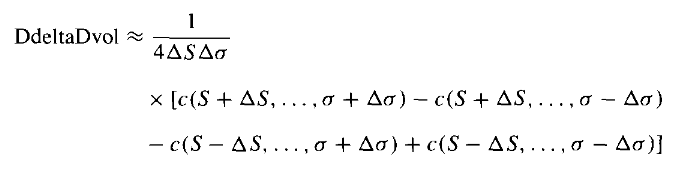
Where: ΔS is change in the underlying, σ is volatility, and c is call price (for a call option).
These Greeks are also known as finite difference approximations.




