A plain vanilla option in which the strike is determined as a percentage of the future/forward price. For instance, a 110% moneyness call would have a strike equal to 110% of the forward price. A 130% moneyness put would have an underlying equal to 130% of the strike, and so on. The value of this option is given in percent of the forward.
In calculation, the value of a moneyness call or put is given by:
c = p= e-rT [N(d1) –L N(d2)]
where L = X/F for a call and L = F/X for a put (X denotes strike and F refers to forward price), and
For example, consider a call option which is 110% out-of-the-money, and has six months to maturity. The risk-free rate is 7%, and volatility is 35%. The value of this option can be calculated as follows:
First of all, L = X/F = 1.1, T = 0.5, r = 0.07, σ = 0.35
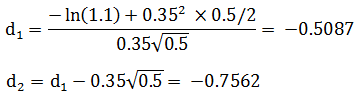
N(d1) = N(-0.5087)=0.2810, N(d2)= N(-0.7562) = 0.2266
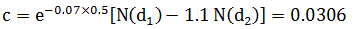
Therefore, the value of a call that is 110% out-of the money relative to the forward price will be equal to 3.06% of the forward price.





Comments