An method/ technique whereby the amortized cost of a financial asset or a financial liability is calculated to the effect that the interest income or interest expense is systematically and uniformly allocated over the period in question. For example, this method is used in amortizing bonds to reach at the actual interest rate (the rate in effect) during any interval over the lifespan of a bond before maturity. Calculation of amortized cost takes into consideration the bond’s book value (initially and going forward at the beginning of any given reporting period). The uniform rate is known as effective interest rate (EIR) and is calculated as follows:
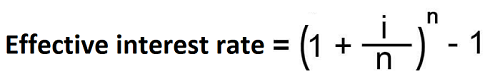
Where i= rate of interest (coupon rate), n= number of periods per year. If interest is paid annually or semiannually, then the number of years should be divided by 1 or 2. The expression in brackets should also be raised to power 1 or 2.
Generally speaking, effective interest method is used for allocating interest expense over the lifespan of financial instruments, using a uniform rate and the market rate to which the instrument is subject. The aim is to reach at the par value of the instrument which is issued either at discount or premium by amortizing interest to the carrying value of the financial instrument.