A third-order greek that captures the rate of change of gamma with respect to changes in the volatility (implied volatility) of a derivative (usually an option). Mathematically, it is the third derivative of the option value, two times to underlying asset price and once to volatility. The following formula gives the value of zomma:
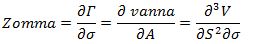
For one unit change in volatility (e.g. from 25% to 26%), zomma need to be divided by 100 (i.e., one basis point).
An investor holding a gamma-hedged portfolio can find zomma useful in anticipating changes to the effectiveness of the hedge as volatility changes.
Zomma belongs to third-order Greeks and is also referred to as DgammaDvol.



