Crypto assets
A crypto asset is a digital asset that represents any digital store of value or medium of exchange (currency) that is stored as entries on the blockchain. It is a digital representation of value or a right that can be transferred or stored electronically (digitally) using distributed ledger technology (DLT) or similar technology. Crypto assets use cryptography (a method to secure data), peer-to-peer networking, and a sort of general ledger to initiate, verify and record transactions. DLT is a technology that enables the decentralized storage, update and validation of encrypted data. One example of DLT are blockchains on which entries are added as ‘blocks’, which form a ‘chain’ that cannot be manipulated or broken. Transactions are recorded on the chain to facilitate verification and provision of proof about existence without the need for a third-party.
In the area of finance and investing, crypto assets provide multiple benefits including the ability to streamline capital-raising processes, enhance competition in the market and create an innovative and inclusive way of financing for various market players (e.g., consumers and SMEs). Crypto assets can be used for investments and/ or payments and for creating coins to fund certain project. These assets can also present opportunities in terms of cost-effective, faster and more efficient payments, in particular on a cross-border basis, by limiting certain redundant layers (intermediaries).
Crypto assets and broadly digital assets represent an essential facet of digitalization, which has been transforming finance and the way business is conducted. The outputs include innovative new products, services, applications and business models. Digital finance plays a key role in shaping and redefining competition, sustainability, and economic resilience. Furthermore, it provides the foundations for more inclusive, modern, prosperous societies.
Crypto assets: main types
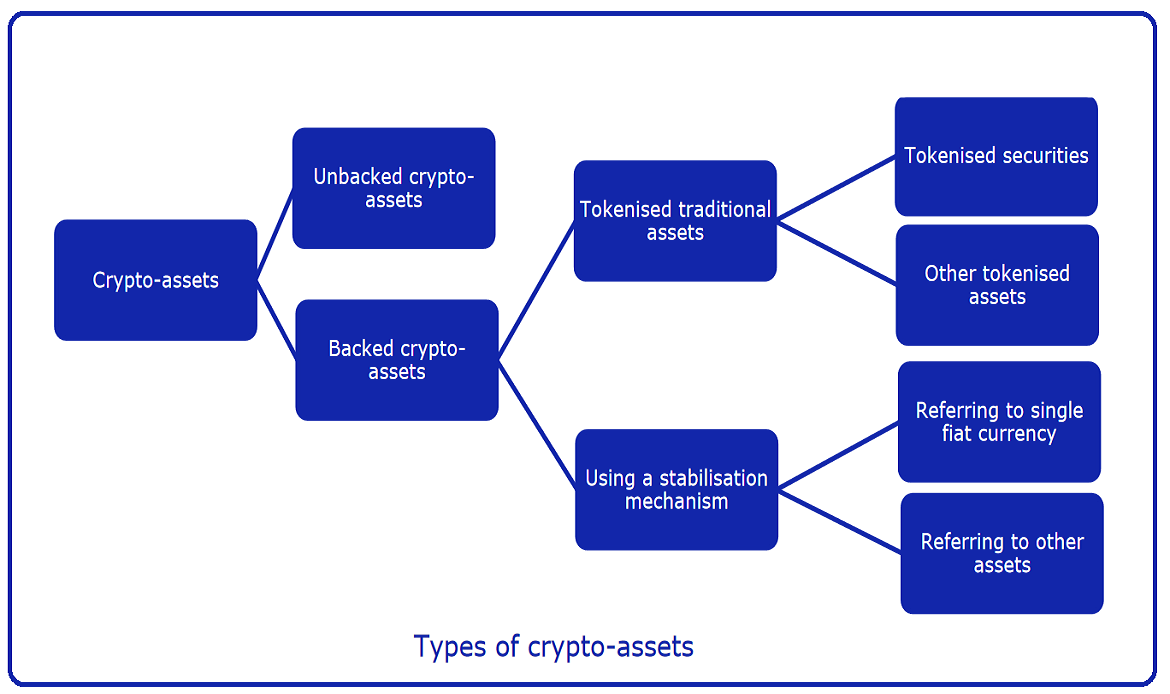
Crypto assets can be classified into multiple types, depending on several defining factors such as use, origination, and asset backing:
- Unbacked crypto assets: such assets that are not backed by an underlying real or financial asset, or other types of digital assets.
- Backed crypto assets: a category of crypto assets that are backed by other assets (real, financial, or even digital). Backed crypto assets are, in turn, divided into tokenized traditional assets (tokenized assets) and assets backed using a stabilization mechanism (stablecoins). Stabilized assets are grouped as those referring to a single fiat currency and those referring to other assets that provide a stable performance over time (for more, see: types of asset-backed tokens). Backed crypto assets also include the distinct category of non-fungible tokens (NFTs)- tokens that can provide a category of asset backing, representing ownership of certain digital assets like digital art, collectibles, or virtual real estate. In turn, NFT-backed tokens can be classified in two categories: hard NFTs, which represent ownership of physical assets connected to the blockchain, or soft NFTs, which represent ownership of digital assets created and maintained on the blockchain.
- Native crypto assets: assets that are created on a blockchain, and hence are considered native (or integral) to the network where it is issued.
- Non-native crypto assets: assets that need to be wrapped (see: wrapping) or validated by a third party before functioning or interacting with a blockchain. The non-native asset is often used to “wrap”, “tokenize,” or represent assets on other networks.