An indicator of momentum valuation that relates the unexpected earnings (earnings surprise) at a given point in time to the standard deviation of past unexpected earnings over a specific period preceding time (t). The standardized earnings surprise (SUE) is usually given by:
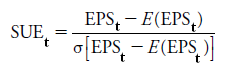
Where: EPSt denotes actual earnings per share at time t; E(EPSt) is the expected earnings per share for time t; σ[EPSt – E(EPSt)] is the standard deviation of the earnings surprise.
In other words, the amount of unexpected earnings is scaled by a measure of the size of historical forecast errors. The smaller the historical size of forecast errors, the more meaningful a specific size of EPS forecast errors, and vice versa.




