A financial ratio that relates the stock price on any given day to earnings per share:
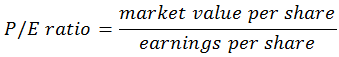
It indicates how much value the market places on a company relative to its earnings. A low P/E ratio may be an indication that the stock is undervalued, whereas a high P/E ratio may imply an overvalued stock. It would be relevant to distinguish between a P/E ratio based on historical data and a P/E ratio calculated using forecasted earnings per share (EPS). In the first case, a high ratio may indicate that investors have high expectations for the company, and vice versa. If the P/E ratio is calculated using forecasts of EPS, and that EPS is lower than the current EPS, then the P/E ratio will be higher than the current P/E ratio, indicating that the market expects earnings to decline.
The P/E ratio is usually used to estimate the equity value of a company using comparable companies. The P/E ratio(s) are multiplied by the earnings of the company whose equity value is being figured out.





Comments