Financial leverage changes a company’s returns and risk. As far as profitability is concerned, financial leverage affects a company’s earning per share (EPS) in two different ways, depending on the level of earnings before interest and taxes (EBIT) relative to a point of reference. Knowing the so-called indifference point is important to determine how profitability is affected by leverage, and so is also knowing where a company’s level of EBIT is relative to it.
The indifference point (also the equivalency point or break-even point of financing) is the level of EBIT at which EPS would be the same between the two given alternatives of financing (debt and equity). If the probability of EBIT dropping below the indifference point is high, the equity alternative should adopted. Conversely, if the probability of EBIT exceeding the indifference point is high, the debt alternative should considered. As a rule of thumb, the lower the probability of downward EBIT variability, the greater the amount of debt can be used, and vice versa.
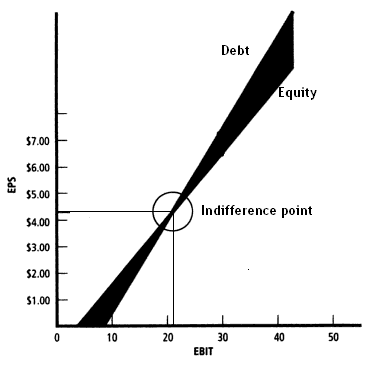
To the left of the indifference point between financing alternatives (where EBIT is lower), financial leverage reduces EPS. To the right of the indifference point (where EBIT is greater), EPS is increased as the company takes on financial leverage.





Comments