A self-referenced credit derivative (a credit contingent swap) in which an issuer sells subordinated debt to an investor and then enters into a total-return swap with the same investor. In the total return swap, the investor pays the subordinate debt total return to the issuer and receives LIBOR plus a spread. The spread is approximately equal to the spread over LIBOR at which the issuer’s senior unsecured debt trades in the secondary market. The following diagram demonstrates this structure, with the spread over LIBOR being 150 basis points.
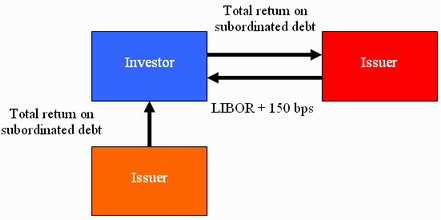
In this sense, the credit contingent swap references one’s own default. A counterparty earns fee income for not defaulting on its debt. However, that counterparty needs to post collateral to back up the exposure for the benefit of the other counterparty. In case of default, the collateral will be seized to satisfy the swap.
This swap is also referred to as a self-referencing credit default swap or a self-referenced credit-contingent swap.