A variance swap in which the buyer (the long) receives, at maturity, the realized daily variance of the reference underlying security/ index weighted by the previous day’s closing price (that is, it is proportional to the underlying price or index reading). The realized variance is determined using the following formula:
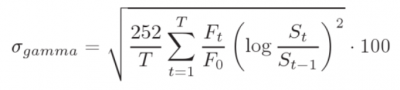
Where: T is time to maturity, Ft is the variance of underlying price/ index at time t, F0 is the variance of underlying price at time 0, St is the underlying price at time t, and S0 is the underlying price at time 0.
Therefore, the buyer is exposed to its price path over the term of the swap. In other words, the buyer has path-dependent exposure to the variance of the underlying price or index reading. Price weighted variance swaps are often less costly than standard/ vanilla variance swaps when the reference security/ index has a downward–sloping skew of implied volatility.
Price-weighted variance swaps have many uses, including particularly the so-called equity dispersion trading (the volatility of a basket or index of securities is traded against the volatility of its components).
This swap is also referred to as a gamma swap or an index price-weighted variance swap.