Swap transactions are typically viewed as the exchange of a fixed rate for a floating rate, or vice versa. Interest rate swaps have the inner ability to convert one interest rate basis to a different interest rate basis, thereby allowing borrowers to secure a synthetic fixed rate or floating rate. The all-in effective rate of a floating-rate loan (or any similar instrument) that has been converted into a fixed-rate loan is equal to the fixed rate paid on the swap plus the spread of the loan:
All-in effective rate = fixed rate on swap + spread on loan
For example, suppose that a company managed to convert a five-year floating rate loan at LIBOR+75 into a fixed rate loan using a swap. The fixed-rate on the swap is 0.8% and it was swapped for LIBOR. The cashflows of the company which are associated with the loan and the swap are shown in the following table:
| Loan interest | (LIBOR + 0.8%) |
| Swap floating rate | LIBOR |
| Swap fixed rate | (7.5%) |
| Effective rate | (8.3%) |
Note: swaps are always concluded against LIBOR flat.
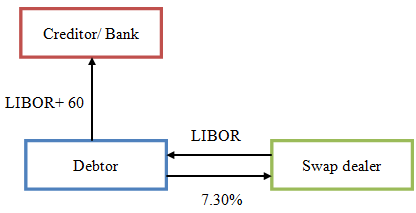
The LIBOR payment pain on the loan is offset by the LIBOR payment received on the swap (swaps are always concluded against LIBOR flat.). The effective rate for the loan after the swap is the fixed rate on the swap in addition to the spread on the loan.





Comments