Concept
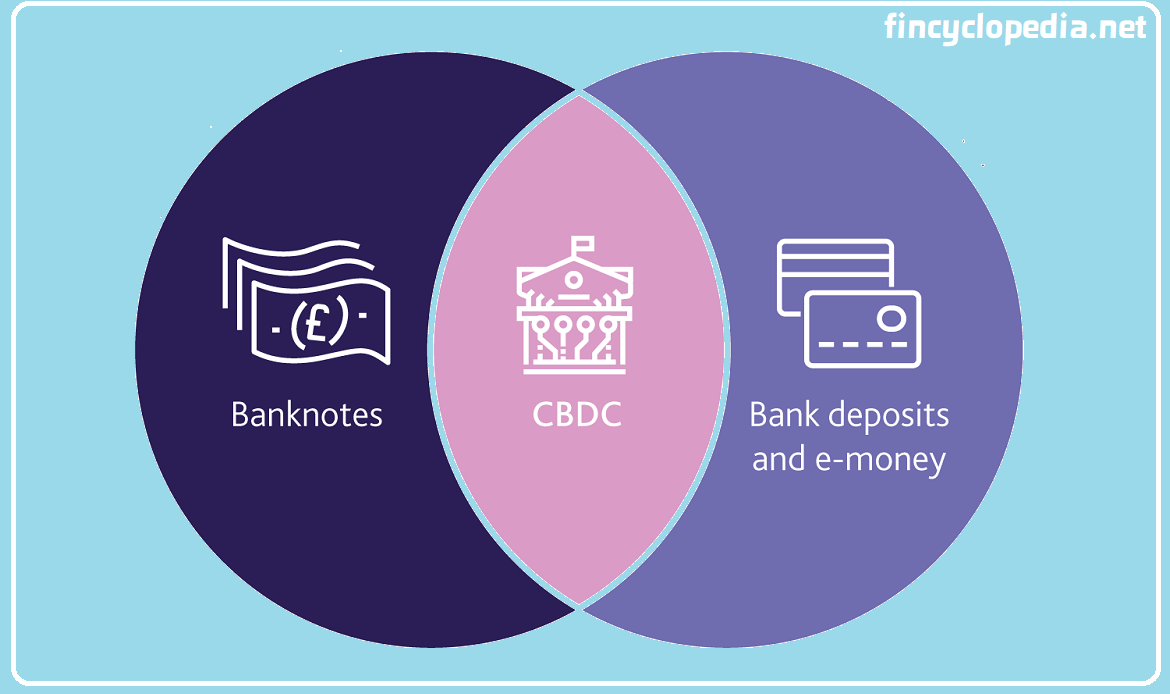
Central bank digital currency (CBDC) is a type of digital money that is issued by a central bank, but is not cryptocurrency and would not replace cash and other types of money under direct control of a central bank. CBDCs are, however, a specific type of virtual currency, and as such carry potential benefits for financial inclusion. Governments and central banks need to be transparent about their release of such currencies, including the potential advantages and risks involved- an essential element for public trust in CBDCs. In an economy, digital money consists of CBDC (a component issued by a central bank) and bank deposits and e-money (issued by commercial banks). The money issued by a central banks encompasses banknotes and coins (in circulation) and CBDCs (issued and held as digital entries).
Forms of money
Money exists in two main forms: central bank money and private money. Money created by central banks is central bank money, typically in the form of banknotes and coins in circulation. Money in its cash or cash equivalent state is currently the only kind of central bank money available to the public. Physical money represents a physical token in the form of coins and banknotes that express value. As a legal tender, central bank money must be accepted by all market participants (and the public at large) if offered in payment within a jurisdiction.
Private money is created by commercial banks when receiving deposits (in the form of banknotes and coins) and reusing it by extending loans to individuals and businesses. As an entry in the bank account, this money can be used to pay by using instruments such as debit or credit cards. The funds deposited can also be withdrawn in the same state money was initially deposited. The relationship between depositors and commercial banks is based on the notion that they can withdraw their funds, virtually any time, and within acceptable limits of risk.
Central bank digital currency components
A central bank digital currency (CBDC) is a digital form of central bank money (i.e., public money issued by a central bank). Essentially, a CBDC system consists of individuals and business (and broadly any type of legal person) having access to a digital currency available to them for transactions and savings accounts, as offered by the central bank in the country in which they operate or are based. In turn, CBDC can classified into retail CBDC (digital money available to individuals and companies) and wholesale CBDC, only available to institutional agents. For retail currency, CBDC consists of a digital representation of coins and banknotes in the form of digital tokens. It is an electronic entry that embodies a specific value belonging to its rightful owner. Having the details of the electronic file, the value can be transferred and a payment can be made in an authenticated process.
Types of central bank digital currency
In terms of the claim, CBDC can be divided into: direct CBDC, indirect CBDC and hybrid CBDC. For direct CBDC (DCBDC), the digital currency represents a claim on the central bank itself, while intermediaries or central banks, per se, carry out the verification process (know your customer, KYC). The central bank also handles the retail payment. An indirect CBDC (ICBDC) places the claim on a market intermediary which is responsible for verification process (KYC) and handles retail payment. The central bank, in which case, only handles wholesale payment. Under the hybrid model, the CBDC is a claim on an intermediary, which is also onboard (KYC) and handles retail payment. The central bank periodically records retail balances.
Synonyms
Central bank digital currency is also referred to as digital fiat currency or digital base money.