An option sensitivity (literally a cross Greek) that measures the rate of change of vega in one underlying in reaction to a change (say, 1%) in the level of another underlying. Mathematically, cross vanna is given by:
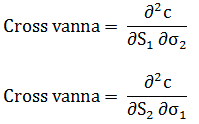
where: c is the option’s value (a call value), S1 is the price/rate of the first underlying, S2 is the price of the second underlying, σ1 is the standard deviation of the first underlying, and σ2 is the standard deviation of the second underlying.
Differently stated, cross vanna measures the rate of change of delta in the second underlying in response to a change in the volatility of the first underlying. Like other cross Greeks, cross vanna is used by traders to calculate the sensitivity for options on two underlyings.





Comments