A financial ratio that relates long-term debt (liabilities) to the sum of long term liabilities and shareholders’ equity. In other words, it is the ratio of debt financed capital to the overall sources of capital (both long-term debt and equity). It is a measurement of an entity’s ability to borrow from the market and pay off the borrowed funds. It is calculated by dividing the amount of debt that it owes to external parties by the total value of its shares:
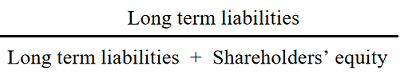
This ratio reflects the ability of an entity to raise capital by means of debt instruments and arrangements (e.g., bonds, notes, debentures, general credit bonds, etc.) Such instruments may be either secured or unsecured. A secured debt implies the existence of a specified collateral for the debt.
This ratio indicates the financial risk that an entity is exposed to due to dependence on external sources of finance. It may indicate to investors (potential buyers of its shares) the amount risk of investing in the shares.





Comments