Put overwriting is an option strategy that involves being simultaneously long stock and short puts on the same share of stock. Plainly speaking, it is constructed by buying shares of stock and writing options against them. For example, an investor might purchase shares of XYZ at $105 and write a $104 put on the same stock. The profit and loss profile of this strategy may be illustrated as follows (assuming the put premium is $4.5):
| Stock price at option expiration date | |||||
| 0 | 70 | 104 | 105 | 130 | |
| Long stock | -105 | -35 | -1 | 0 | 25 |
| Short put | -100.5 | -30.5 | 3.5 | 4.5 | 29.5 |
| Profit/loss | -205.5 | -65.5 | 2.5 | 4.5 | 54.5 |
The following exhibit illustrates the above scenario:
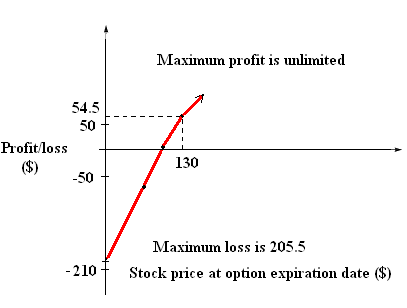
If prices exceed its strike price, the put will expires worthless, while the investor earns proportional profits on the increasing stock price. But if prices move down, the investor’s loss will be magnified because the stock is losing value and the short put position will result in progressively increasing liabilities.




