The sale of accounts receivables at a discount to a third party called the factor with recourse (i.e., a recourse factoring) or without recourse (i.e., a non-recourse factoring). Factoring has many types including: conventional factoring, maturity factoring, full service factoring, credit factoring (invoice discounting), bulk factoring, agency factoring, notification factoring (disclosed factoring) and non-notification factoring (undisclosed factoring/ confidential factoring).
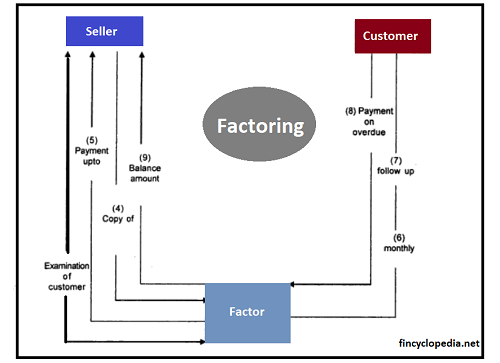
The flow of factoring process involves three parties: the seller (of receivables/ debt), the factor, and the customer (originally owing money to the seller):
A real-life example of factoring is the credit card company, where the factoring transaction has the following three parties:
- the credit card issuer (the factor).
- the cardholder (the customer).
- the trader (seller of debt)