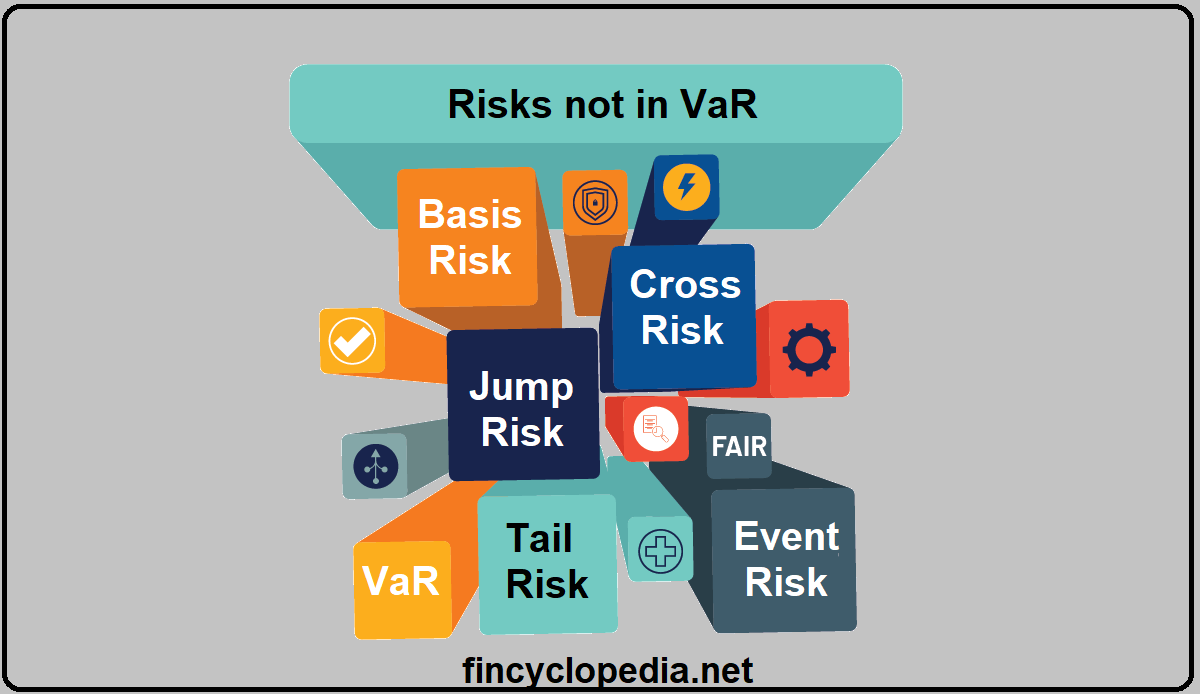
Risks not in value at risk (VaR) are those risks/ risk factors that are not captured or covered by VaR. Examples of such risks include extreme risks or tail risks (outliers), non-linear risks, volatility risk, jump risk, and to some extent liquidity risk.
Risks not in value at risk (RNIV) is a concept in risk management introduced by the UK Financial Conduct Authority (2010) to tackle the risks not covered by the VaR model.
As a framework, RNIV is designed to ensure that a bank’s own funds are made ready to meet all risks which are not captured at all or not captured adequately, by the firm’s VaR and stressed VaR models. These risks include, but are not limited to, missing and/ or illiquid risk factors such as basis risks, cross-risks, higher-order risks, and calibration parameters.
The RNIV framework is also intended to account for event risks that could adversely affect the entity’s operations and activities.