Also known as minimum variance hedge ratio (MVHR); a mathematical tool for determination of the optimal cross hedging ratio. This means the minimum variance between the gain/ loss associated with the cash position and the loss/ gain on the futures position. Effective hedging reflects the maximum reduction in the variance- i.e., the amount of variability in the cash position that is eliminated by the futures position.
The output of MVHR is the number of futures contracts required to account for the effect of price sensitivity variance during a specific period of time.
This ratio is determined using a number of methods including regression analysis, naive method, etc. When MVHR is one (a very basic assumption that does not hold in reality), then the ratio is known as naive hedge ratio.
This ratio is usually calculated using the following formula:
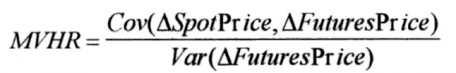
Where: Cov and Var denote covariance and variance, respectively.
Using regression analysis, it can be given using the following formula:
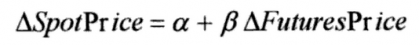
Where MVHR is captured in beta (slope of the equation). It measures the effectiveness of the hedge: the larger the slope, the more effective the hedge, and vice versa.



