Joint staking
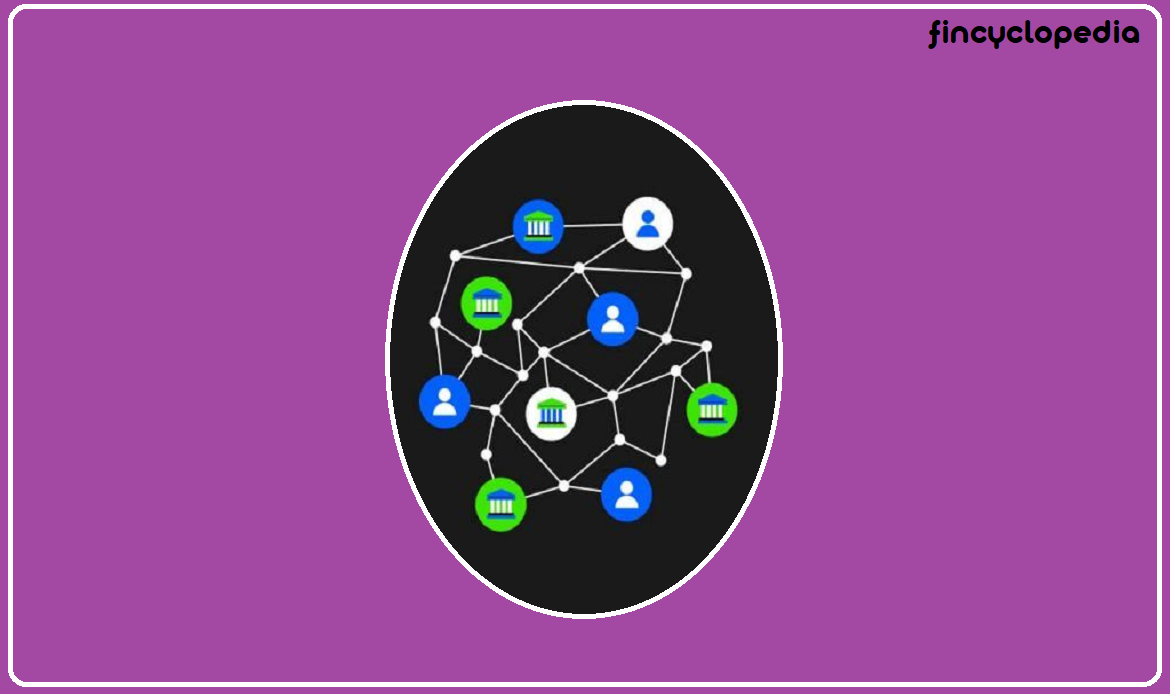
Joint staking refers to a collaborative approach where multiple participants pool their resources to stake (lock up) assets in a blockchain network, combining their staking power over the lock-up period and increasing the potential of earning rewards (and more rewards). With combined resources minimum staking requirements can be comfortably met. Furthermore, this strategy can reduce the risk embedded with staking smaller sizes. In short, individual investors can follow this strategy to achieve a scale that only larger players in the market can provide for. Joint staking works out to benefit both experienced users and beginners, as it forges a sense of community and shared objectives while also spreading out potential risks amongst users, rather than concentrating on a few. Rewards are shared by participants often in proportion to their contributions to the pool of staked assets (digital assets). Overall, joint staking aims to incentivize larger participation and make the staking process accessible to market participants, even those who may not have sufficient individual resources or technical know-how. The process may involve techniques such as smart contract, whereby staking and distribution of rewards would be transparent and fairer to participants. Joint staking may be based on participation by multiple stakers pooling their staked coins together and having the respective node hosted at the network to validate transactions and create blocks, while rewards are transparently and fairly shared.
Self-custody staking
Self-custody staking (or self-custodial staking) is a type of staking in which a single validator (miner) node conducts staking for its own coin (the network coin), independently validating transactions and creating blocks, and producing rewards in that coin or token. By self-custody, users can exercise full control over their staked assets, as opposed to joint staking which requires relinquishing a certain degree of control over assets to the hosting party. A user or participant plays the role of a custody for his/ her own staked digital assets. Staking is the process whereby network participants can earn rewards (or returns) by locking their cryptoassets and other digital assets in wallets. Decentralized finance (DeFi) applications and protocols require a certain level of liquidity to ensure transactions are carried out in a smooth and efficient manner. As a distinct asset class, cryptoassets are increasingly staked, and nowadays provide an attractive means to earn passive investment income on such assets, whether individually or as part of an investment scheme. Staking utilizes a mechanism known as a proof-of-stake (PoS) consensus, being an alternative consensus mechanism to proof of work (PoW) for blockchains.
Self-custody staking is carried out by holding a minimum number of assets (cryptocurrencies) and running a node to participate in validating transactions on the blockchain network. The participants can ensure control over their staked asset, staking roles are usually divided between two categories of participants: stakers and validators. Holders of assets use credentials and permissions related to the staked assets. Validators, on the other hand, host the respective node and hold permissions related to node management. This division can ensure the security, stability, and continuous rewards of the node. Stakers, as ordinary users, must have some technical knowledge and ability to handle security measures to ensure the stability and security of the node.