A standard power option has a nonlinear payoff at maturity. The payoff of a call (power call option) is:
Power call payoff = Max [Si – X, 0]
The payoff of a put (power put option) is:
Power put payoff = Max [X – Si, 0]
Where i is some power (i > 0).
The value of a power call option is given by the following equation (see Heynen and Kat, 1996c; Zhang, 1998; and Esser, 2003):
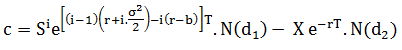
Similarly, the value of a power put option is given by:
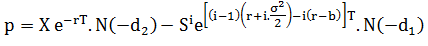
Where:
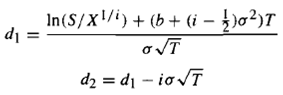
For example, consider a power call option with three months to maturity. The current underlying price is $10, the strike price is $100, the risk-free interest rate is 7%, the continuous dividend yield is 5.5%, and the expected volatility of the underlying stock is 40%. Raising to power 2, the value of this call would be calculated as follows:
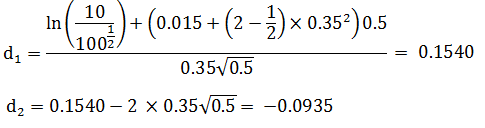
Plugging in d1 and d2 values, we find:
N(d1) = N (0.1540) = 0.5596, N(d2) = N(-0.0935) = 0.4641
The value of the power call option is:
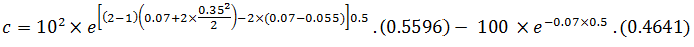
c= 15.88
If the above option is a put, its value would be:
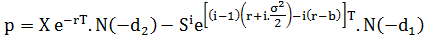
Plugging in d1 and d2 values, we find:
N(-d1) = N (-0.1540) = 0.4404, N(-d2) = N(0.0935) = 0.5359
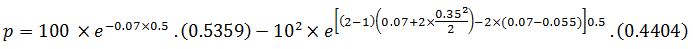
If the above option is a put, its value would be:
p= 11.14




