A credit default swap (CDS) in which the reference entity is not a third party. More specifically, the credit risk of one of the parties is referenced to the credit swap transaction. Most commonly, the seller assumes the role of the reference entity. For example, a company may purchase protection against the default of a bank from the bank itself. However, if the credit quality of the selling party deteriorates, the present value of the swap would rise at the same time. Generally, the protection buyer would be exposed to the correlation risk of the reference entity and the simultaneous default of the party that would pay the cash settlement amount.
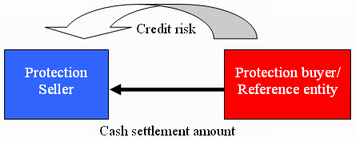
The protection buyer can confine entering into a self-referencing CDS to protecting instrument such as a credit-linked note (CLN) that is issued and paid up-front or sufficiently collateralized by the protection seller. The seller, on the other hand, may be able to gain an extra yield, i.e., the protection fees paid by the buyer.